Canadian Home Sales Edge Upward in August
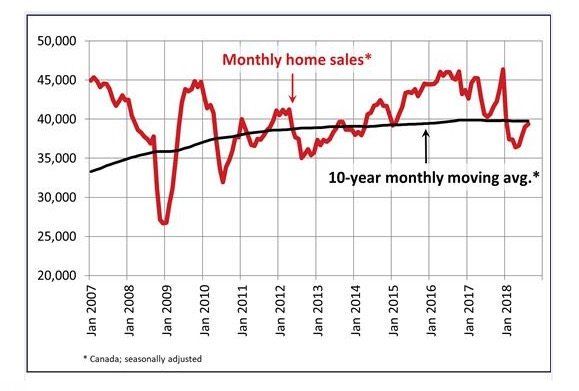
The Canadian housing market showed continued signs of stabilizing last month with sales edging upward and prices easing a bit. National home sales increased 0.9% in August, the fourth consecutive monthly gain. Sales in Toronto advanced 2.2% while they rose 2.9% in Vancouver. Nevertheless, the pace of sales activity remains below levels in most other months going back to 2014 (see chart below). As well, recent monthly sales increases are diminishing, which could mean that the recent rebound, particularly in Ontario, could be running out of runway.
The housing market has been recovering from steep sales declines early this year after federal regulators imposed stricter mortgage lending rules and the central bank raised borrowing costs. Home sellers also seem to be lowering prices for homes, fueling demand.
Roughly half of all local markets posted an increase in sales from July to August, led again by the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), along with gains in Montreal and Edmonton. Sales in the major urban areas of BC declined by 3.8% year-over-year (y/y) in August. The housing market in BC has slowed considerably since the February provincial budget hiked the foreign purchase tax and suggested a speculation tax could be introduced in the fall.
New Listings
The number of newly listed homes was unchanged between July and August, as new supply gains in the Greater Vancouver Area (GVA) and Montreal offset declines in the GTA and Winnipeg.
With sales up slightly and new listings unchanged, the national sales-to-new listings ratio edged up to 56.6% in August compared to 56.2% in July. The long-term average for this measure of market balance is 53.4%.
Based on a comparison of the sales-to-new listings ratio with the long-term average, about two-thirds of all local markets were in balanced market territory in August 2018.
There were 5.2 months of inventory on a national basis at the end of August 2018, right in line with the long-term average for the measure.
Home Prices
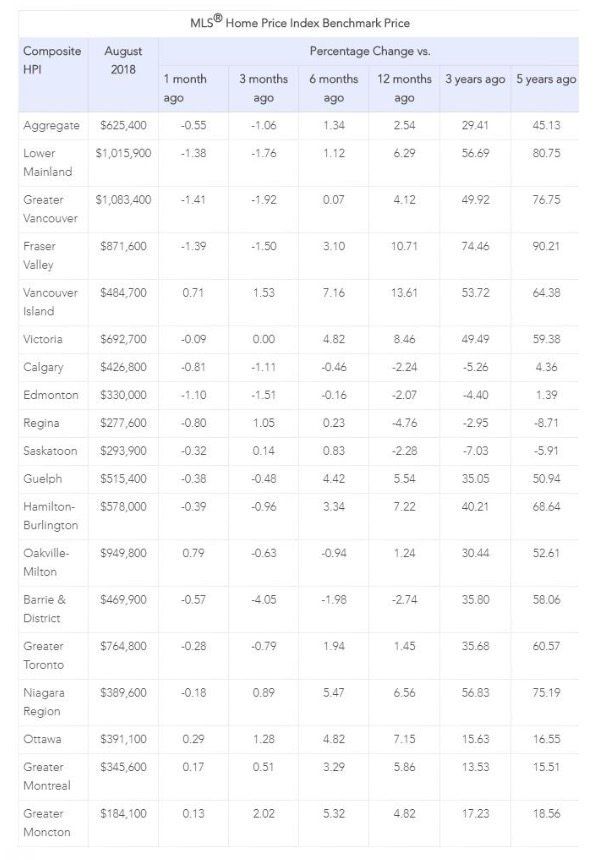
The Aggregate Composite MLS® Home Price Index (MLS® HPI) was up 2.5% y/y in August 2018, well below the booming pace in 2016 and early 2017. Benchmark home prices fell by 0.6% from July to August, the biggest decline since August of last year. The price decline was driven by Vancouver, where prices dropped 1.4%, the most significant monthly drop in a decade. Toronto home prices fell 0.3% in August.
Condo apartment units posted the most substantial y/y price gains in August (+9.5%), followed by townhouse/row units (+4.3%). Meanwhile, one-storey and two-storey single-family home prices were little changed on a y/y basis in August (+0.4% and -0.4% respectively).
Trends continue to vary widely among the 17 housing markets tracked by the MLS® HPI. Home price gains are diminishing on a y/y basis in the Lower Mainland of British Columbia (GVA: +4.1%; Fraser Valley: +10.7%). Prices in Victoria were up 8.5% y/y in August. Elsewhere on Vancouver Island, prices climbed 13.6%.
Among the Greater Golden Horseshoe (GGH) housing markets tracked by the index, home prices were up from year-ago levels in Hamilton-Burlington (+7.2%), the Niagara Region (+6.6%), Guelph (+5.5%), the GTA (+1.4%) and Oakville-Milton (+1.2%). By contrast, home prices remained down on a y/y basis in Barrie (-2.7%).
In the Prairies, benchmark home prices remained down on a y/y basis in Calgary (-2.2%), Edmonton (-2.1%), Regina (-4.8%) and Saskatoon (-2.3%).
Meanwhile, home prices rose by 7.1% y/y in Ottawa (led by an 8.2% increase in two-storey single-family home prices), by 5.9% in Greater Montreal (driven by a 6.3% increase in two-storey single-family home prices) and by 4.8% in Greater Moncton (led by a 7.5% increase in two-storey single-family home prices). (see Table below)
Bottom Line
Housing markets continue to adjust to regulatory and government tightening as well as to higher mortgage rates. The speculative frenzy has cooled, and multiple bidding situations are no longer commonplace in Toronto and surrounding areas. The housing markets in the GGH appear to have bottomed, and supply constraints may well stem the decline in home prices in coming months. The slowdown in housing markets in the Lower Mainland of BC accelerated last month as the sector continues to reverberate from provincial actions to dampen activity, as well as the broader regulatory changes and higher interest rates.
Since the implementation of new mortgage standards, nonprice lending conditions for mortgages and home equity lines of credit have also tightened. Additional rate hikes by the Bank of Canada are coming this fall, likely in late-October if the NAFTA negotiations appear to be progressing. The economy is running at full capacity, unemployment is low, and incomes are rising. Inflation is expected to return to the Bank of Canada’s 2% target, and uncertainty regarding trade with the US remains, but the central bank will continue to cautiously raise its trend-setting interest rate through the end of next year.
This article was written by Dr. Sherry Cooper DLC’s Chief Economist.